Detection of Nigrospora sphaerica in the Philippines and the susceptibility of three Hylocereus species to reddish-brown spot disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56890/jpacd.v22i.321Keywords:
Dragon fruit; ITS gene; H. megalanthus; H. polyrhizus; H. undatus.Abstract
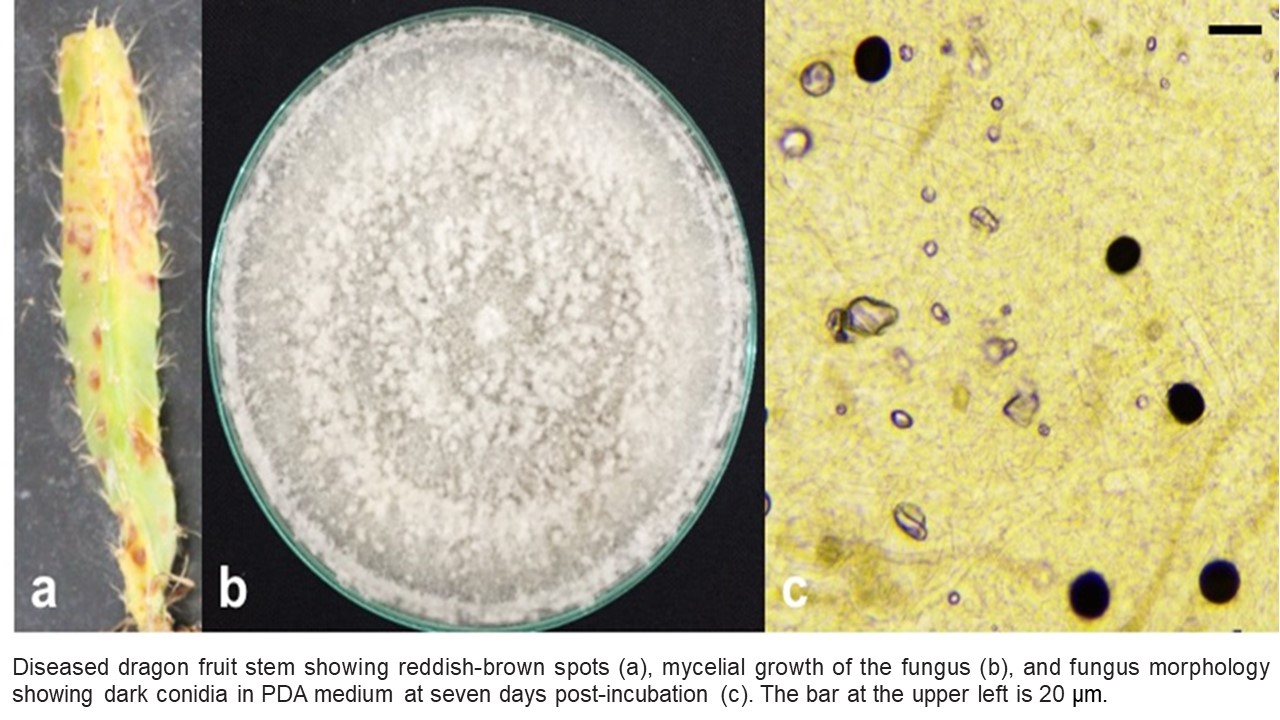
Diseases are among the major problems that negatively affect dragon fruit profitability worldwide. Diseases of dragon fruit in the Philippines are yet to be identified and reported. This study elucidates the causal agent of a disease infecting stems of dragon fruit grown in Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines. The fungus was isolated and identified as Nigrospora sp. based on morphological and cultural characteristics in potato dextrose agar medium. Using the DNA sequence of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) gene region, isolate MBDF0016b was identified as Nigrospora sphaerica. The Philippines strain was closely related to the Malaysian strain, which also causes reddish-brown spot in dragon fruit (H. polyrhizus), and to other N. sphaerica isolates from other host-plant species. Nigrospora sphaerica MBDF0016b was pathogenic to H. megalanthus, H. undatus, and H. polyrhizus in detached stem and glasshouse assays. The same fungus was re-isolated from the inoculated stems and thus, establishing Koch’s postulate. This paper is the first confirmed scientific record of a dragon fruit disease in the Philippines and the first report of N. sphaerica as a dragon fruit pathogen causing reddishbrown spot disease in H. megalanthus.
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
Indexed in
- Academic society
- Journal of the Professional Association for Cactus Development
- Publisher
- Professional Association for Cactus Development