Characterization of mucilage from clones of Opuntia and Nopalea prickly pear cactus harvested in different seasons in Brazilian semiarid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56890/jpacd.v23i.457Keywords:
Nopalea cochenillifera; Opuntia stricta; mucilage; infrared; principal component analysis (PCA); conservation.Abstract
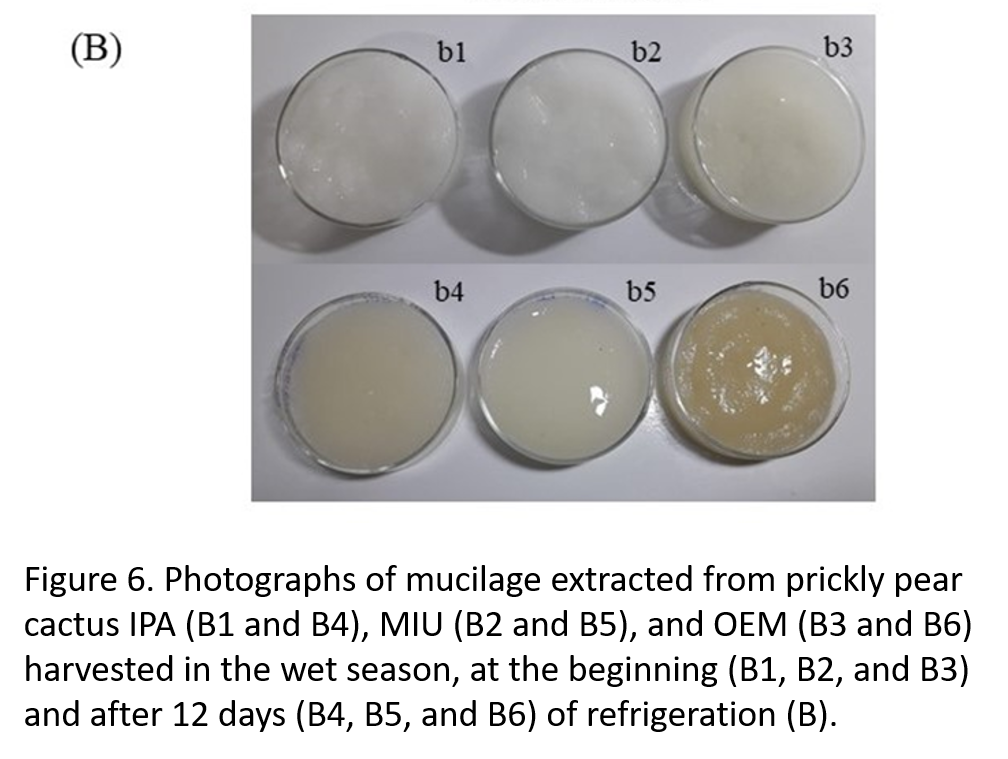
This study proposes to characterize hydrated and refrigerated mucilage obtained from cladodes of clones of prickly pear cactus harvested during the drizzle and dry seasons in the semiarid of Brazil. Cladodes of Opuntia stricta [Haw.] Haw (Orelha de Elefante Mexicana [OEM] clone) and Nopalea cochenillifera Salm Dyck (IPA Sertânia [IPA] and Miúda [MIU] clones) were harvested at 6 am and extracted mucilage. The main bands in the infrared region were characterized. Physicochemical analyses were performed on day zero and at 12 days. Cladodes harvested in the dry season showed higher mucilage yield and soluble solid, total soluble carbohydrate, and K+, for the three clones. The OEM clone also exhibited significant increases in pH, Na+, and electrical conductivity when harvested in the dry season than in the wet season. In addition, the mucilage extracted from the Opuntia cladodes did not have changes in the carbohydrate, titratable acidity, or total soluble protein levels. The IPA and MIU clones, in turn, were characterized by parameters that remained stable during conservation (phenolic compounds, titratable acidity, K+ and Na+). The spectroscopic profile was similar for all studied clones. The principal component analysis allowed the formation of clusters between seasons and conservation times. It is suggested that the cladodes of the genus Nopalea showed better potential in the manufacture of edible films and coatings. The cladodes of the genus Opuntia, for the use of mucilage as ingredients in foods such as bread, pasta, and others, making them with better functional properties. Therefore, these factors should be considered for the use of mucilage in the industry.
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
Indexed in
- Academic society
- Journal of the Professional Association for Cactus Development
- Publisher
- Professional Association for Cactus Development