Anaerobic co-digestion of Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill. cladode with cow manure: Effect of different cultivars on biochemical methane potential
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56890/jpacd.v24i.453Palabras clave:
Nopal cultivars, co-digestion, energy crop, bioenergy, Gompertz modelResumen
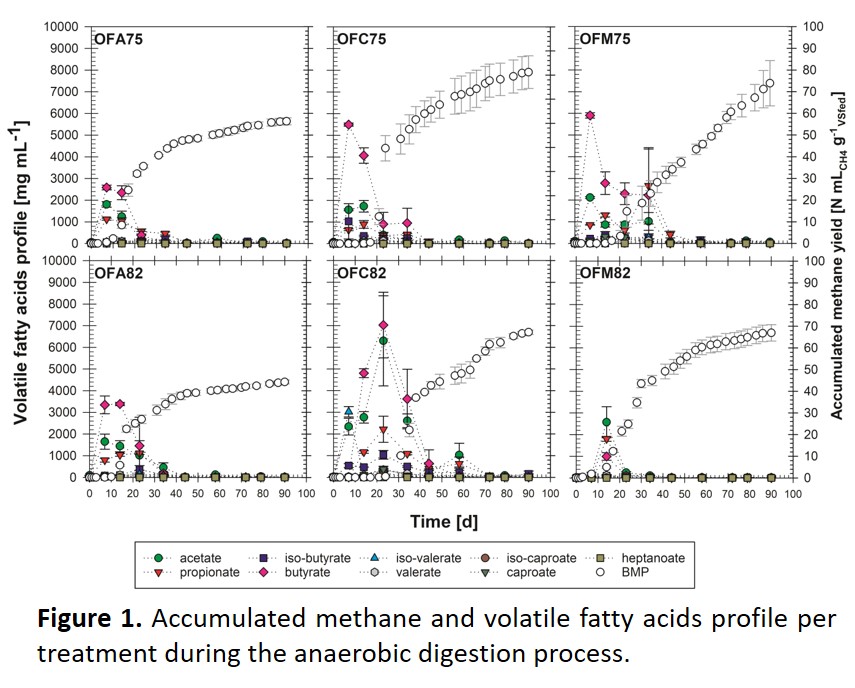
Nopal (Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill.) cladode has garnered great interest recently in the area of agro-energy as emerging biomass due to its sustainable production. The objective of this study was to compare the biochemical methane potential of different nopal cultivars in co-digestion with cow manure. For this purpose, two different nopal cladodes: cow manure proportions (75:25 and 82:18) and three different cultivars (Atlixco, Copena V1, and Milpa Alta) were evaluated. The results indicated that the treatments with higher biochemical methane potential (mL CH4 g-1 VSfed) were Milpa Alta 75:25 (71.4), Copena V1 75:25 (66.5), Milpa Alta 82:18 (64.6), and Copena V1 82:18 (59.0), which showed no statistical difference (P>0.05) between them, whereas the Atlixco treatments (75:25 and 82:18) had the lowest (P<0.05) values (52.8 and 41.5, respectively). The results suggest that the cow manure proportion and nopal cultivar used in a co-digestion system may influence its biochemical methane potential.
##plugins.generic.pfl.publicationFactsTitle##
##plugins.generic.pfl.reviewerProfiles## N/D
##plugins.generic.pfl.authorStatements##
Indexado: {$indexList}
-
##plugins.generic.pfl.indexedList##
- ##plugins.generic.pfl.academicSociety##
- Journal of the Professional Association for Cactus Development
- Editora:
- Professional Association for Cactus Development