Leaf production and gel quality of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. F. under irrigation regimens in northern Mexico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56890/jpacd.v24i.497Palabras clave:
Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f.; soil moisture content; irrigation; crop yields; gel quality.Resumen
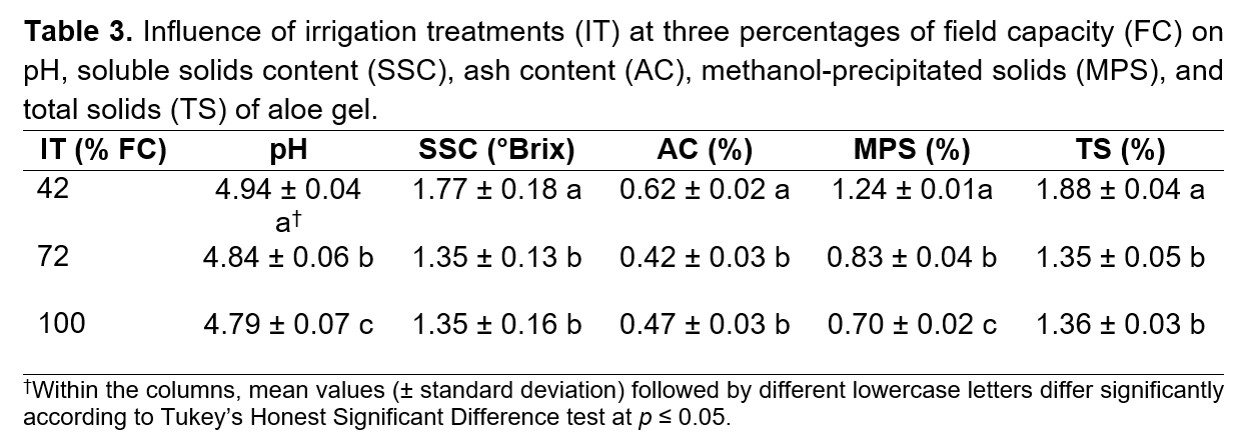
The derivatives of aloe plant leave [Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f.], such as gel, juice, and powder, are highly appreciated in the industrial sector. This study evaluated the effect of different soil moisture contents on the growth, production, and gel quality of aloe grown in an arid region of Mexico. The study was conducted in a randomized complete block design with three replicates. Base on the percentage of field capacity (FC), three irrigation treatments were tested: 42%, 72%, and 100% of FC corresponding, on average (± standard deviation), to 0.12 ± 0.02 m3 m-3 (as control), 0.18 ± 0.02 m3 m-3, and 0.24 ± 0.02 m3 m-3 of soil water content, respectively. Aloe plants watered with 72% of FC had greater plant height and leaf width than plants watered at 42% of field capacity, while plants with 100% of FC treatment had the longest (56.1 cm) and thickest (1.5 cm) leaves. Aloe plants irrigated at either 72% or 100% of field capacity produced the freshest leaf biomass and gel. In contrast, plants grown at 42% of field capacity treatments had the highest pH (4.94), total soluble solids (1.77 °Brix), ash content (0.62%), methanol-precipitated solids (1.24%), and total solids (1.88%) of aloe gel. Even though the lowest soil moisture content (42% of field capacity) reduced plant and leaf growth and leaf and gel yields, gel quality was enhanced, meeting the gel quality standards demanded by the international market.
##plugins.generic.pfl.publicationFactsTitle##
##plugins.generic.pfl.reviewerProfiles## N/D
##plugins.generic.pfl.authorStatements##
Indexado: {$indexList}
-
##plugins.generic.pfl.indexedList##
- ##plugins.generic.pfl.academicSociety##
- Journal of the Professional Association for Cactus Development
- Editora:
- Professional Association for Cactus Development